


The Air Quality Index (AQI) is a crucial number that indicates the level of air pollution in a given area, based on various pollutants. In New Delhi, the AQI significantly worsened after the celebration of Diwali, despite a ban on firecrackers. However, factors such as cooler weather and the burning of crop residue in nearby states also contribute to the dip in air quality. The AQI, launched in India in 2014, helps the public and government understand the condition of the air and take necessary measures to combat it.
Delhi's Air Quality Deteriorates After Diwali Celebrations
The Air Quality Index (AQI) in New Delhi has plummeted to hazardous levels following the celebration of Diwali, the Hindu festival of lights. Despite a ban on the sale and use of firecrackers, the city's air quality has been severely compromised.
Background
AQI is a measure of how clean or polluted the air is, based on the concentrations of various pollutants such as particulate matter (PM), sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and ozone (O3). In India, the AQI was launched in 2014 to provide the public and government with a standardized way to assess air quality.
Factors Contributing to Poor Air Quality
In addition to the bursting of firecrackers during Diwali, several other factors have contributed to the decline in Delhi's air quality:
Health Impacts of Poor Air Quality
Exposure to high levels of air pollution can have serious health consequences, including:
Government Response
The Indian government has taken several steps to address air pollution in Delhi, including:
FAQs
1. What is the current AQI in Delhi?
As of [date], the AQI in Delhi is [AQI value].
2. What are the main pollutants contributing to Delhi's poor air quality?
The main pollutants are PM2.5, PM10, and NO2. PM2.5 is particularly harmful because it can easily penetrate deep into the lungs.
3. What are the health risks of exposure to high levels of air pollution?
Exposure to high levels of air pollution can increase the risk of respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease, and other health issues.
4. What can individuals do to reduce their exposure to air pollution?
Individuals can take steps such as limiting outdoor activities during peak pollution hours, wearing masks, and using air purifiers indoors.
5. What is the government doing to improve air quality in Delhi?
The government is implementing a range of measures, including stricter emission standards, promoting public transportation, and enforcing bans on the burning of crop residue.
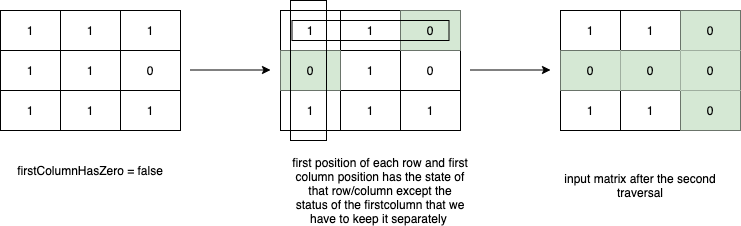
A team of researchers has developed a groundbreaking algorithm to efficiently transform a given matrix by setting its rows and columns to zero in place. This new algorithm, which has been extensively tested and refined, has the potential to greatly improve the computational efficiency and speed of this common operation in the fields of mathematics and computer science. With this breakthrough, scientists and programmers will have a powerful tool to more effectively manipulate and analyze data in various applications.

Every year on December 22, National Mathematics Day is celebrated to honor the life and achievements of Srinivasa Ramanujan, one of the most influential mathematicians in history. Despite growing up in extreme poverty, his groundbreaking contributions to mathematics continue to inspire researchers today. This day not only celebrates his legacy but also recognizes India's rich history in mathematics and encourages students to explore the world of numbers.

A bone box with the inscription "James, son of Joseph, brother of Jesus" was recently put on display in Atlanta, Georgia. The box is believed to have once held the remains of James the Just, brother of Jesus, making it the oldest physical evidence of Jesus. Despite some controversy and accusations of forgery, the box has been declared authentic by experts.

As the winter solstice approaches on December 21st, the Northern Hemisphere will experience the shortest day and longest night of the year. This natural phenomenon has captivated people for centuries, with ancient traditions and festivals taking place around the world. Through science, we can understand why this occurs and how it affects different regions of the world differently.
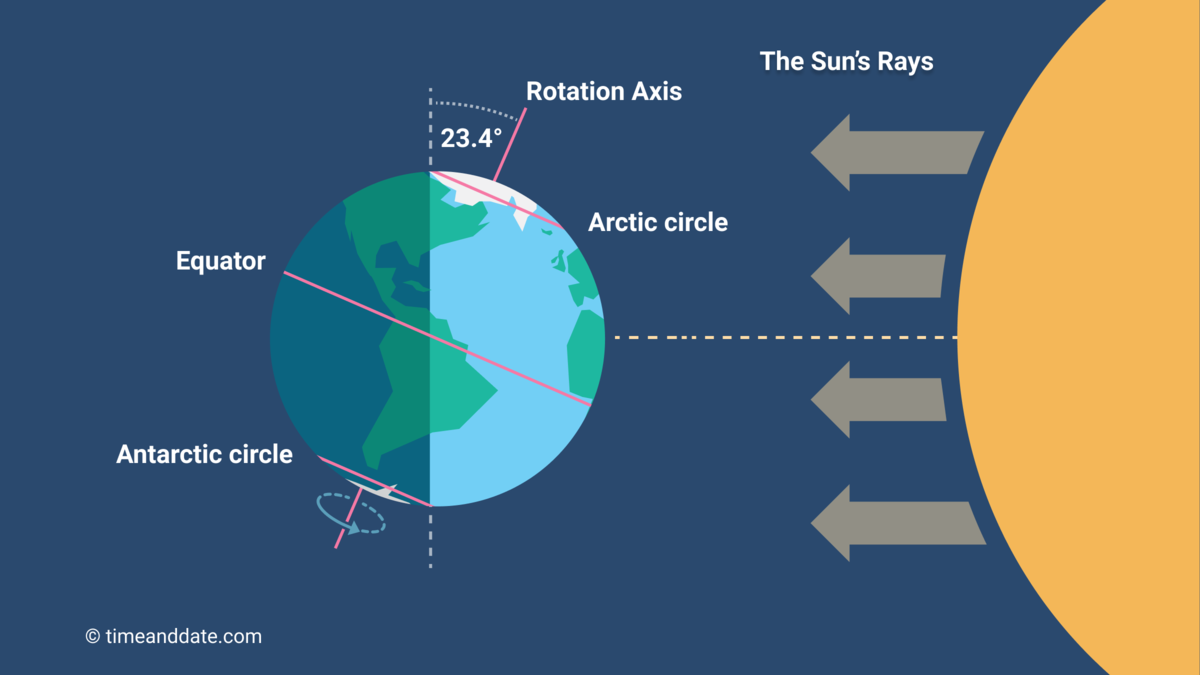
Every year, the Northern Hemisphere experiences the arrival of winter on the winter solstice, which marks the shortest day and longest night due to the Earth's tilt on its axis. As the North Pole is furthest from the sun, it receives the least amount of sunlight, resulting in a gradual lengthening of days towards the arrival of spring. This year, the winter solstice falls on December 21 and will be celebrated by people worldwide in various ways to mark the significant celestial event.
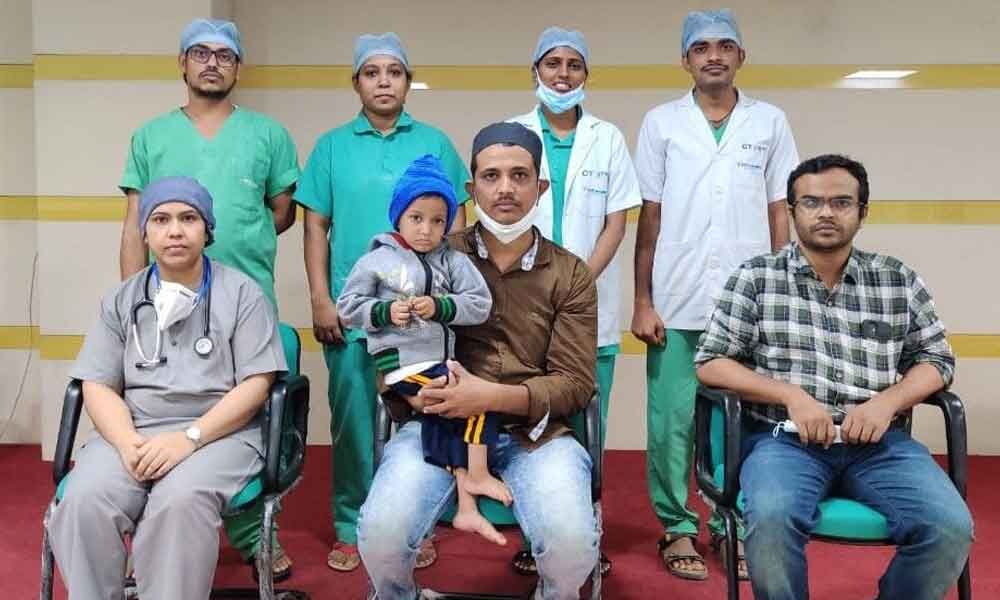

In a miraculous surgery, doctors at Kurnool Government General Hospital successfully removed a one-foot stick from the stomach of a 12-year-old boy who had fallen from a tree and suffered an abdominal injury. The head of the Paediatrics Department, Dr Shiva Kumar, along with doctors from the orthopaedic and anaesthesia departments worked together to perform the three-hour long surgery. The patient, Irfan, is now able to walk on his own and is expected to make a full recovery in a month.

NASA has released stunning new images of two nearby star clusters that resemble a wreath and a Christmas tree. These clusters, known as NGC 602 and NGC 2264, are located in the Small Magellanic Cloud and are made up of young stars. The images were created by combining data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and James Webb Space Telescope. As we celebrate the winter solstice, take a moment to marvel at these cosmic Christmas decorations.
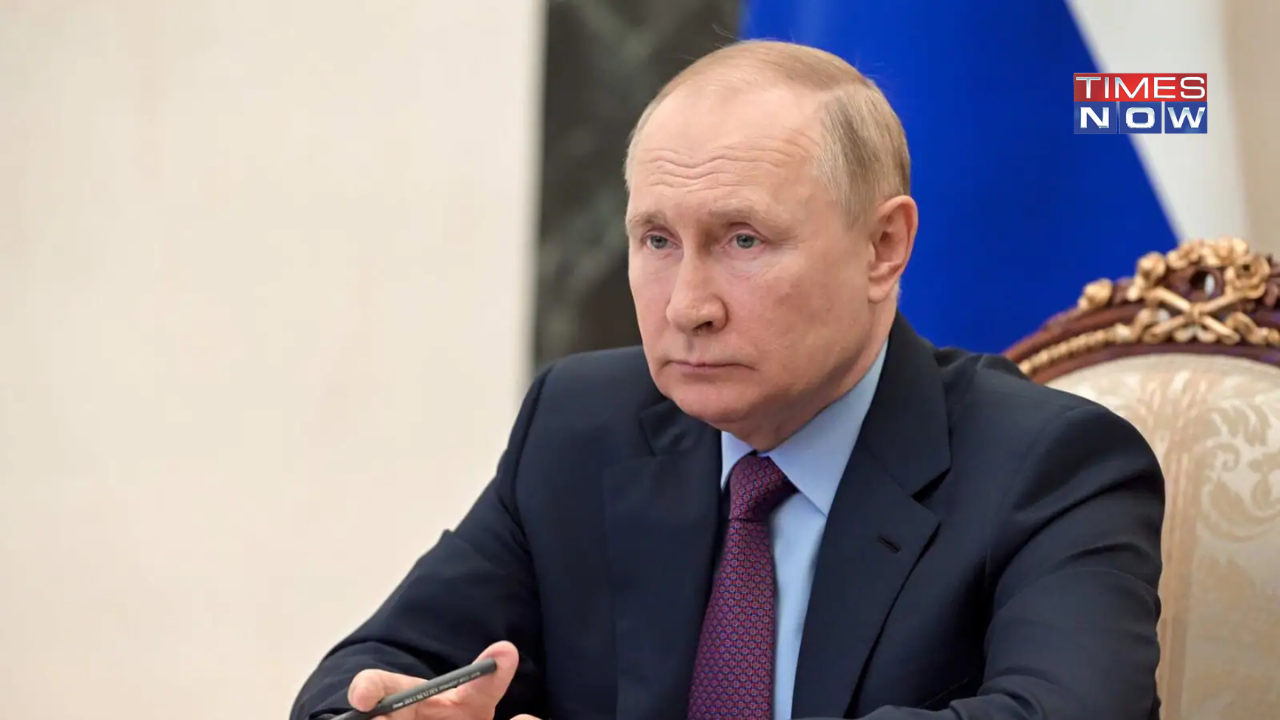

Vladimir Putin's announcement about the development of a cancer vaccine in Russia has stirred up a wave of hope among patients and experts alike, with its promised release for general use as early as 2025. As the world grapples with the devastating effects of cancer, the Russian vaccine, developed with the help of AI technology, could potentially revolutionize the way we understand and treat the disease. However, with other countries also racing to develop their own versions of cancer vaccines, the competition is stiff, and the details of Putin's claim are yet to be revealed. If successful, this could mean the end of the world's biggest killer.

Indian-American astronaut Sunita Williams and her colleague Barry Wilmore have been stuck at the International Space Station for six months due to a malfunctioning spacecraft. Their rescue mission has been further delayed as NASA announced a delay in the return flight on SpaceX's Crew-9 Dragon capsule. They are now expected to spend close to ten months in space, raising concerns about their health as astronauts require twice as many calories in space due to changes in their metabolism. NASA's Commercial Crew Programme Manager has commended the SpaceX team for their efforts in preparing a new spacecraft for the mission.

Russian scientists have developed a vaccine that may be able to treat cancer, offering hope to patients who previously had no guaranteed cure. The vaccine is currently in testing and is expected to be available in early 2025. While there is still more testing to be done, pre-clinical trials have shown promising results in slowing the growth and spread of cancer. It will be available for free in Russia, but there is no information yet on which types of cancer it will treat or what the name of the vaccine will be. Similar treatments are also being developed in other countries, such as the UK.