


The Human:Nature campaign led by The Nature Conservancy has raised over $50 million for conservation efforts in Indiana, surpassing its initial goal by $2 million. This successful fundraising initiative has allowed TNC to protect 10,000 acres of land, plant 140,000 trees, improve visitor experiences at nature preserves, and promote sustainable agriculture practices in the state. Additionally, the Mining the Sun strategy has been implemented to repurpose mine lands and brownfields for renewable energy projects. This campaign showcases the crucial connection between humans and nature, and the positive impact conservation efforts can have on both.
The Human:Nature Campaign: Preserving Indiana's Natural Heritage
Background
The Human:Nature campaign, spearheaded by The Nature Conservancy (TNC), was launched in 2017 to protect and enhance Indiana's natural ecosystems. The campaign aimed to raise $50 million to support conservation initiatives across the state. This includes efforts to preserve critical habitats, promote sustainable agriculture practices, and enhance visitor experiences at nature preserves.
Success and Impact
The Human:Nature campaign has been a remarkable success, surpassing its initial goal by $2 million. To date, TNC has protected 10,000 acres of land, planted 140,000 trees, and improved visitor experiences at nature preserves. The campaign has also supported the implementation of sustainable agriculture practices, such as cover cropping and no-till farming.
Mining the Sun Strategy
A key component of the Human:Nature campaign is the Mining the Sun strategy. This innovative approach repurposes mine lands and brownfields for renewable energy projects. By converting these degraded sites into solar and wind farms, TNC is generating clean energy while also restoring the natural landscape.
Human-Nature Connection
The Human:Nature campaign highlights the vital connection between humans and nature. By protecting natural ecosystems, we are not only safeguarding the environment but also creating opportunities for recreation, education, and economic growth. The campaign recognizes the importance of investing in conservation efforts that benefit both people and wildlife.
Top 5 FAQs
What is the Human:Nature campaign?
How much money has the campaign raised?
What has the campaign achieved?
What is the Mining the Sun strategy?
Why is the Human-Nature connection important?

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is offering internship opportunities for graduate and postgraduate students in the field of science and engineering. These programmes aim to provide hands-on experience in cutting-edge research and development in defence technology. Interested candidates between the ages of 19 and 28 with relevant degree backgrounds can apply for these internships, which range from 4 weeks to 6 months. However, selected candidates will have access only to unclassified areas and there is no guarantee of employment after the training period.
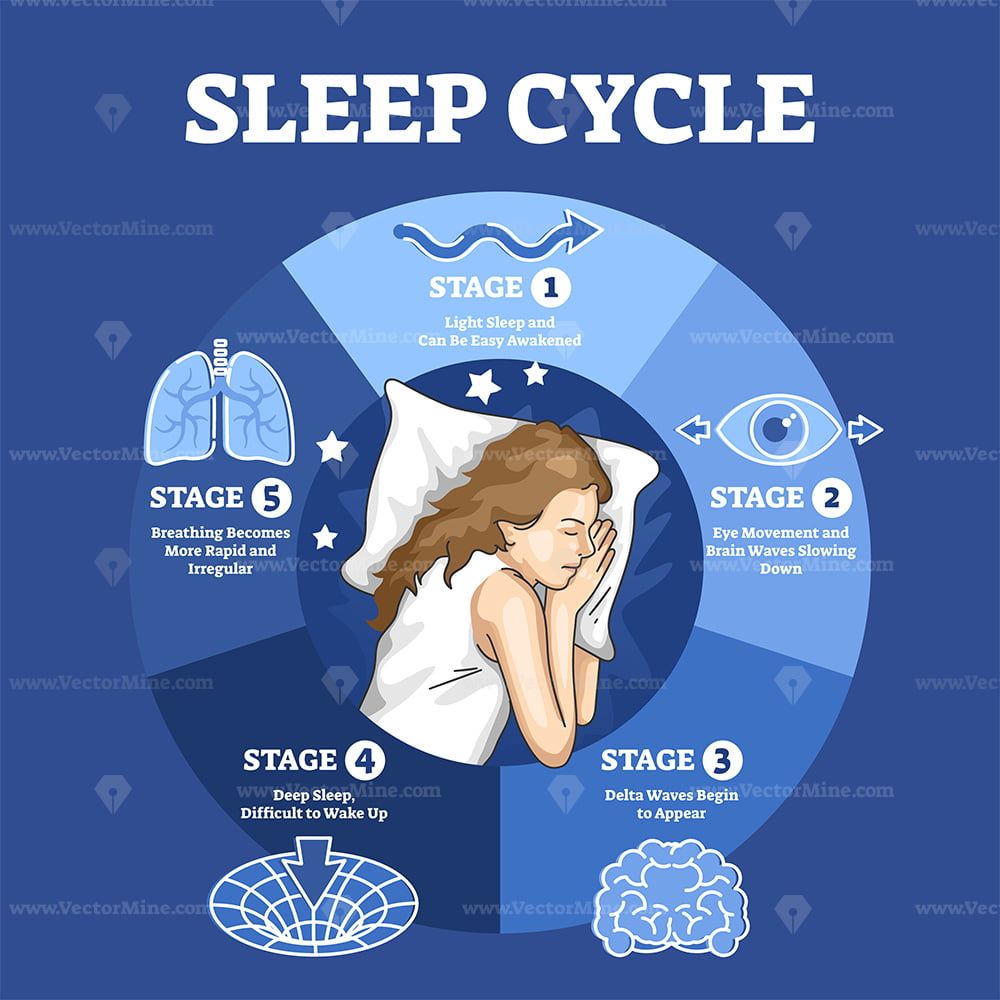
An earthquake with a magnitude of 4.0 struck Delhi early this morning, shaking residents awake and causing widespread fear and uncertainty. While some may brush off the eerie phenomenon of being woken up just before the quake, there may be some truth to humans having the ability to detect seismic activity. According to experts, our brains are subconsciously attuned to environmental changes, making us more likely to wake up or experience sleep disturbances before an earthquake strikes. Furthermore, earthquakes can have long-lasting effects on our sleep patterns, leading to chronic sleep disturbances and potential mental health issues such as anxiety and depression.
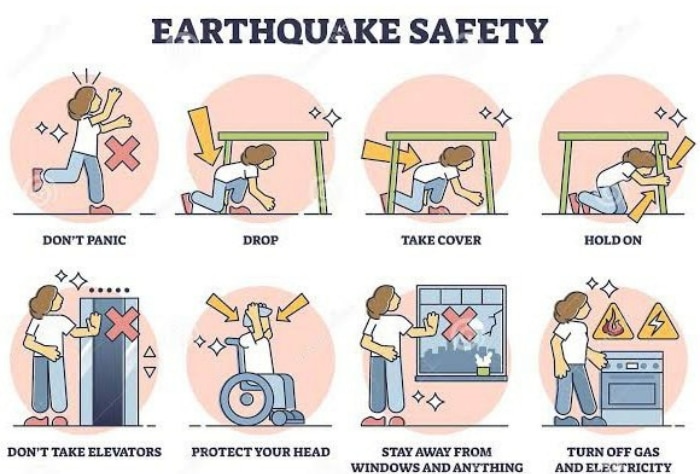
The recent earthquake in Delhi, with a magnitude of 4.0, has caused panic among residents of the National Capital Region. Experts have explained that the epicentre being in Delhi itself is the reason for the strong tremors felt. They have also emphasized the importance of taking safety precautions and following guidelines from NDMA and BMTPC, such as exiting small buildings and taking cover in larger ones.

Delhi was sent into a frenzy on Monday morning when a 4.0 magnitude earthquake rattled the city. The epicentre of the quake was near Durgabai Deshmukh College of Special Education in Jheel Park, Dhaula Khan. No casualties were reported, but residents were left shaken by the force of the tremors, with some witnessing uprooted trees and damage to properties. The National Centre for Seismology is actively monitoring the situation in Delhi-NCR, which is known to be part of an active seismic zone.
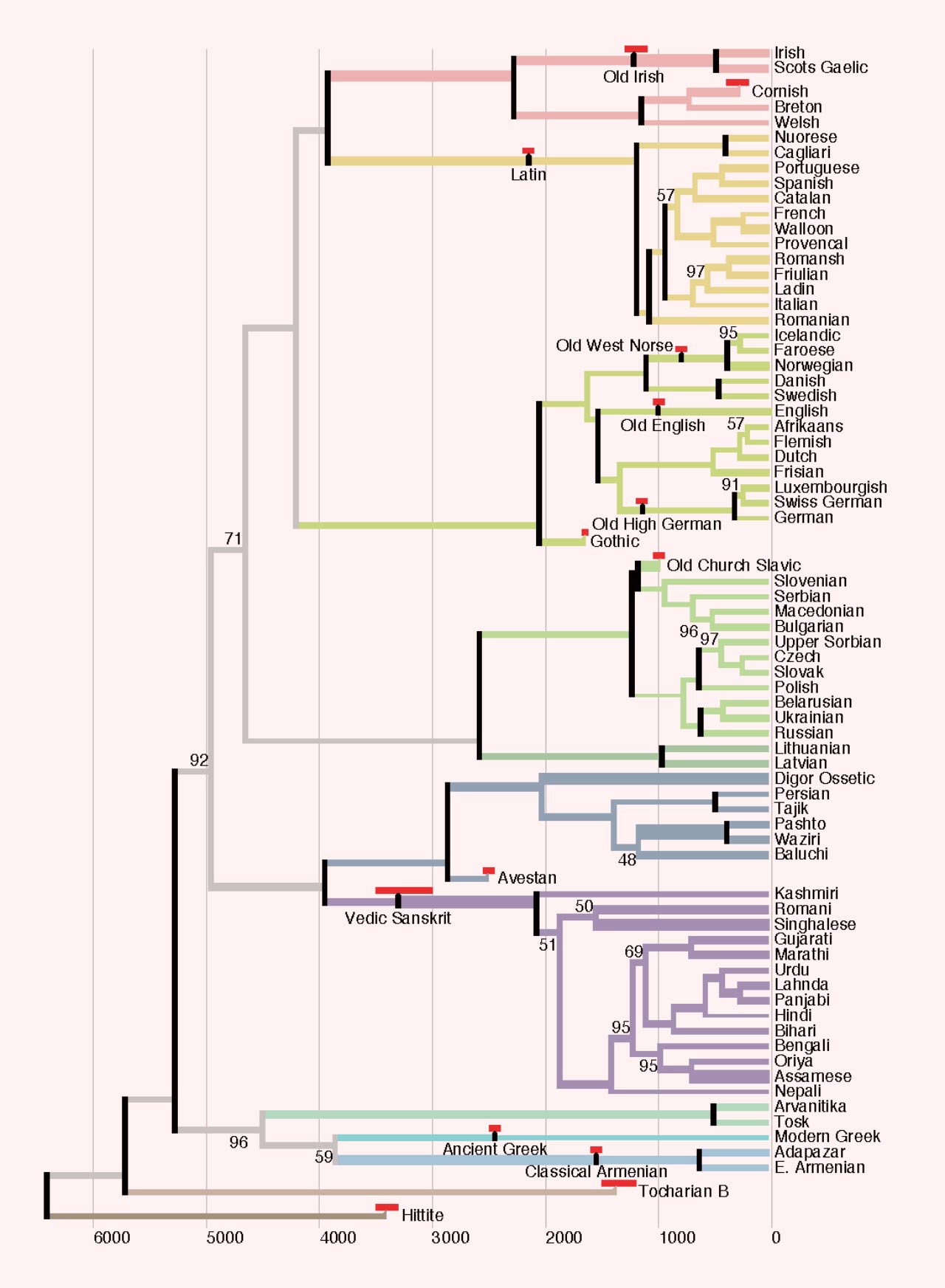
A new study published in Nature by Russian and Ukrainian scientists challenges the long-standing narrative about the origins of Indo-European languages like Sanskrit, Hindi, and Urdu. By analyzing DNA from ancient individuals across Eurasia, the researchers propose a migration route from the Eurasian Steppe that played a significant role in spreading language and culture. This study sheds light on the complex history of Indo-European language evolution and challenges traditional beliefs about the influence of Aryans.

From a young age, the author's fascination with the natural world led them to pursue a career in science. However, as they progressed, they noticed the lack of female representation in STEM fields, particularly women of color. This not only has negative impacts on inclusivity and diversity, but also leads to products and research that do not accommodate female needs. The author argues that celebrating and including women in STEM is crucial for driving innovation, addressing societal challenges, and ensuring diverse perspectives are integrated into scientific and technological progress.

While recording a podcast with tech millionaire Bryan Johnson, Zerodha's Nithin Kamath was shocked by the air quality in Mumbai's Bandra area. With an AQI of over 160, Nithin's Instagram post shed light on India's air pollution crisis beyond the commonly associated city of Delhi. He also called for researchers to collaborate and address the long-term health risks associated with breathing in polluted air. Nithin also suggested a policy to link real estate prices to AQI levels to prioritize public health.
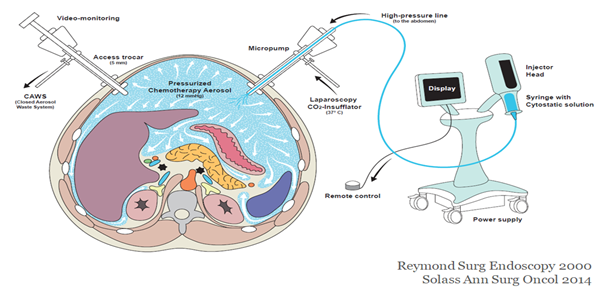
Dr Jitender Rohila, a renowned surgeon and consultant at Fortis Hospital, explains the cutting-edge surgical procedures of HIPEC and PIPAC, which are transforming the treatment of peritoneal surface cancers. These techniques involve delivering heated chemotherapy directly to the abdominal cavity or aerosol chemotherapy under pressure, resulting in improved drug absorption and reduced side effects. While HIPEC is suitable for patients who have undergone cytoreductive surgery for abdominal cancers, PIPAC offers promising options for those with advanced diseases or seeking additional treatment after surgery.
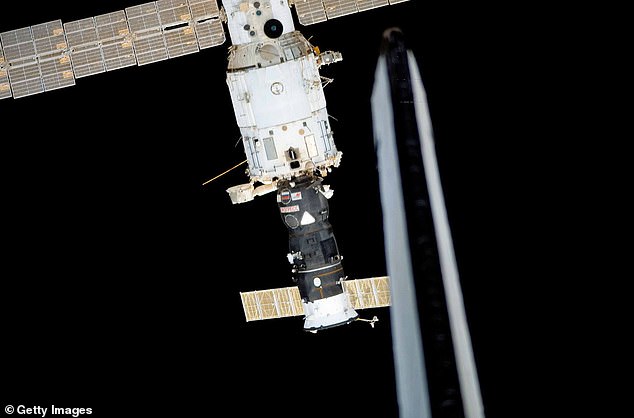

NASA and Roscosmos are on high alert as cracks in the Russian service module on the ISS continue to worsen, posing a top safety risk. Despite efforts to contain the air leak since 2019, the source remains unknown and has reached record high levels this year. As a precaution, astronauts have been instructed to stay close to their spacecraft, and access to the module has been limited to critical use only. NASA is also working on an emergency evacuation plan for American astronauts, highlighting the urgency of this critical situation. With the ISS facing an increased risk from orbital debris and operating beyond its intended lifespan, the future of the station remains uncertain.