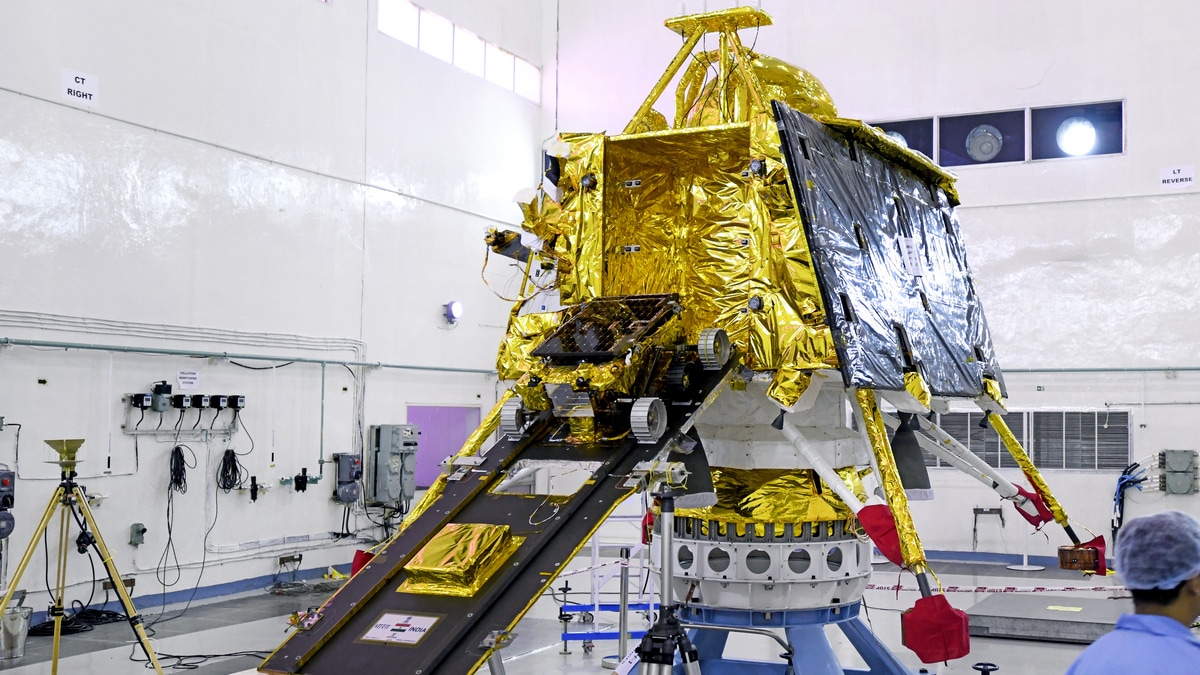



Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully placed two satellites, weighing 220kg, into a circular orbit of 475 km for a crucial space docking technology demonstration. This mission also included the launch of POEM-4 with 24 payloads from startups, industries, and academia. Scientist S Somanath stated that the docking process is expected to take place on January 7, after operations at ISTRAC Bengaluru from December 31. This mission is a major step towards future space missions for India.
Space Docking: India's Technological Leap into the Future
Introduction
Space docking, the process of two spacecraft connecting in orbit, is a crucial technology for future space exploration missions. The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) recently achieved a significant milestone in this field with the successful launch of two satellites for a space docking demonstration.
ISRO's Space Docking Experiment
On December 31, 2022, ISRO launched two 220-kg satellites into a circular orbit of 475 km. The satellites are equipped with advanced navigation, guidance, and control systems. The docking process is expected to take place on January 7, 2023, after operations at the Indian Space Tracking and Control Centre (ISTRAC) Bengaluru.
This mission is a major step towards future space missions for India. It will demonstrate the country's capabilities in autonomous rendezvous and docking, which are essential for complex space operations such as satellite servicing, repair, and assembly.
Historical Background
The concept of space docking has been around for decades, but it has only been successfully implemented a few times. The first successful space docking was achieved in 1966 by the Soviet Union's Soyuz-1 and Soyuz-2 spacecraft. Since then, other countries, including the United States, Russia, and China, have also demonstrated their space docking capabilities.
Importance of Space Docking
Space docking is a critical technology for a variety of reasons:
FAQs
1. Why is space docking so important?
Space docking is important because it enables a variety of complex space operations, including spacecraft assembly, repairs, satellite servicing, scientific research, and space tourism.
2. Who has achieved space docking before?
The Soviet Union, the United States, Russia, China, and now India have successfully demonstrated space docking capabilities.
3. What are the challenges of space docking?
Space docking is a complex process that involves autonomous navigation, guidance, control, and precision rendezvous. Ensuring a successful and safe connection between two spacecraft in orbit is a significant technological challenge.
4. What is the significance of ISRO's space docking demonstration?
ISRO's successful launch and upcoming docking experiment demonstrate India's growing capabilities in space exploration and satellite technology. It is a major milestone towards future complex space missions and positions India as a leading player in the global space race.
5. What are the future applications of space docking?
Future applications of space docking include assembling and servicing modular space stations, repairing damaged satellites, conducting scientific experiments in space, and enabling space tourism.
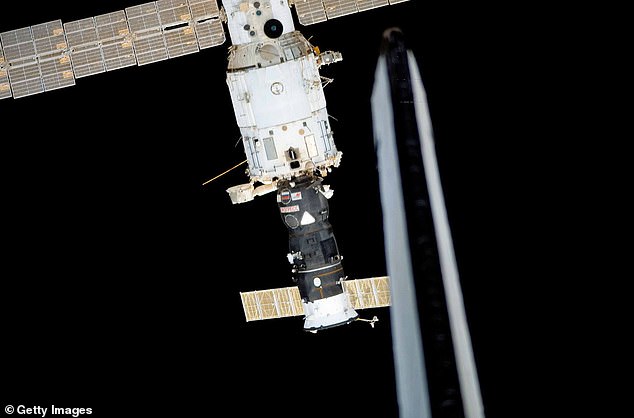

NASA and Roscosmos are on high alert as cracks in the Russian service module on the ISS continue to worsen, posing a top safety risk. Despite efforts to contain the air leak since 2019, the source remains unknown and has reached record high levels this year. As a precaution, astronauts have been instructed to stay close to their spacecraft, and access to the module has been limited to critical use only. NASA is also working on an emergency evacuation plan for American astronauts, highlighting the urgency of this critical situation. With the ISS facing an increased risk from orbital debris and operating beyond its intended lifespan, the future of the station remains uncertain.
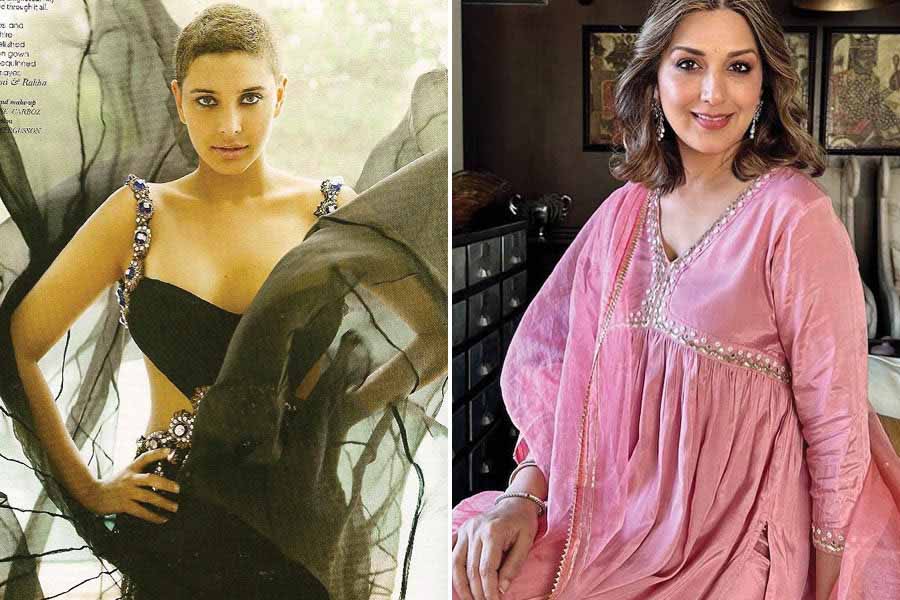

On World Cancer Day, actress Sonali Bendre, who battled cancer in 2018, talks about the importance of early detection and praises the government's Ayushman Bharat initiative for breaking financial barriers and providing accessible and affordable healthcare for cancer patients. Filmmaker-writer Tahira Kashyap and actor Emraan Hashmi also commended the Ayushman Bharat and Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY) for making cancer treatment accessible regardless of financial background, on this international day aimed at reducing preventable suffering from cancer.

Learn about the ancient Ayurvedic practices that can lead to a healthier and happier start to your day. From waking up during Brahma Muhurat to practicing deep breathing exercises and having a light and warm breakfast, Ayurveda offers various ways to boost your overall well-being. Start incorporating these 8 morning routines into your daily routine for a blissful and energized start to your day.

A team of academics has uncovered valuable insights into Roman legal proceedings through a newly discovered papyrus dating back over 1,880 years. The papyrus, named after Professor Hannah Cotton Paltiel who discovered it, reveals how the Roman empire handled financial crimes involving slaves in Judaea and Arabia. It is the longest Greek papyrus ever found in the Judean desert and sheds light on the prosecutors' notes and trial preparations before the Bar Kokhba revolt.

A metal detectorist in Westphalia, Germany has unearthed a one-of-a-kind find – a tiny gold lock that dates back to the Roman era. Measuring less than half an inch in diameter, this miniature version of a typical Roman lock was likely used to secure precious belongings. With the help of 3-D neutron computed tomography, archaeologists have been able to examine the lock's intricate inner workings, shedding light on its design and functioning. This remarkable discovery raises questions about the prevalence and significance of such precious miniature locks in Roman society.

The annual census of dolphins at Chilika lake in India's eastern state of Odisha has begun, with over 100 people participating in the three-day exercise. Equipped with specialized equipment, a team of retired government officials, researchers, students, and experts are counting the dolphins at India's largest brackish water lagoon. The census aims to track the population of the endangered species, which is listed on the International Union for the Conservation of Nature's Red List. Last year's data was not released due to adverse weather conditions, but in 2023, 173 dolphins of two species were found in the lake. The census is being carried out by the Chilika wildlife division in collaboration with the Chilika Development Authority.

* A team of scientists has developed a new algorithm for calculating the power function, making the process more efficient and accurate. This development could have far-reaching implications for fields such as engineering, physics, and economics, where power calculations are common. Using this new algorithm, researchers can now quickly and accurately determine power values, helping to advance their research and innovations. Furthermore, this method ensures that the resulting values are always non-negative, eliminating the need for post-processing.
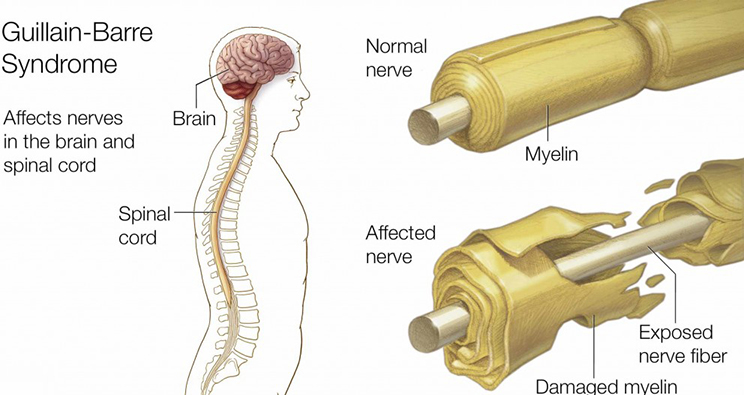
As Maharashtra continues to battle against infectious diseases like HMPV and bird flu, health experts are now raising alarm over the rising cases of Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS) in several cities of the state. While some studies have linked GBS to the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine, others have refuted this claim. However, one thing is clear - GBS is a serious medical emergency that requires immediate treatment to prevent paralysis or even death. A doctor has also shared important tips on how to prevent foodborne illnesses, which can also be a cause of GBS.
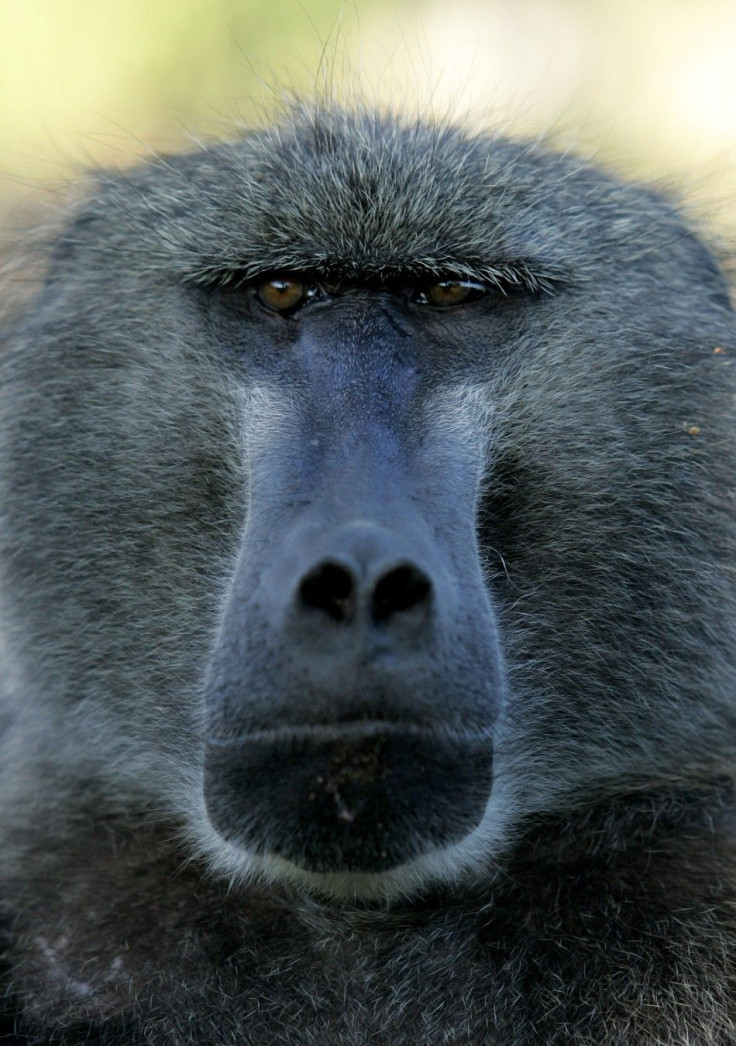

In the animal kingdom, being an alpha male may seem like the ultimate achievement, but a new study shows that for baboons, it comes with intense levels of stress. Despite having dominance, respect, and first dibs on resources, these primates live in constant fear of losing their position and must guard their mates from rival males. This takes a toll on their physical and mental well-being, showing that being at the top is not as great as it may seem.

The city of Mumbai has been put on high alert by the Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation following reports of Guillain-Barré Syndrome cases in nearby Pune. With Mumbai being at risk of potential cases, hospitals have been urged to be prepared with adequate ICU beds and ventilators. This comes as a precautionary measure to ensure the city is well-equipped to handle any potential outbreak.