


On November 30, 2024, China successfully launched two experimental satellites using the Long March-12 carrier rocket. This will support their coordinated tasks of space station application and development, as well as deploying their internet satellite mega constellation. In 2024, China's manned space program will also launch the Shenzhou-18 manned spacecraft to further advance their advancements in space technology and connectivity.
China's Space Launch Program: Advancements and Future Prospects
China's space program has made significant strides in recent years, with a focus on developing launch vehicles and spacecraft for various missions.
Recent Launches and Milestones
On November 30, 2024, China successfully launched two experimental satellites using the Long March-12 carrier rocket. These satellites are intended to support the development and operation of China's space station, as well as the deployment of its satellite internet mega constellation.
Additionally, in 2024, China's manned space program will launch the Shenzhou-18 manned spacecraft. This mission aims to further advance China's capabilities in space exploration and strengthen its role as a global leader in space technology.
Background
China's space launch program began in the 1950s, with the development of rockets for scientific and military purposes. The program gained momentum in the 1970s, with the launch of China's first satellite, Dong Fang Hong 1, in 1970.
Since then, China has made steady progress in developing its launch capabilities. The Long March series of rockets has become China's primary launch vehicle, with different variations designed for different payload capacities and mission requirements.
In addition to launch vehicles, China has also made significant advances in spacecraft development. The country has successfully launched and operated numerous satellites, including communications, navigation, Earth observation, and scientific research satellites.
Top 5 FAQs and Answers
1. What is the significance of China's space launch program?
China's space launch program has strategic importance for the country, as it enables the development of various space technologies and applications. It supports national security, economic growth, and scientific research.
2. What are China's future space exploration plans?
China has ambitious plans for future space exploration, including crewed missions to the Moon and Mars. The country also plans to establish a permanent human presence in space and explore the possibility of interplanetary travel.
3. How does China's space program compare to other major spacefaring nations?
China's space program is among the most advanced in the world. The country has made significant progress in launch vehicle development, spacecraft manufacturing, and astronaut training. However, it still lags behind the United States and Russia in terms of overall space capabilities.
4. What are the potential risks and challenges associated with China's space launch program?
The development and launch of rockets and spacecraft involve inherent risks and challenges. These include technical failures, launch accidents, and the potential for space debris. China has taken significant steps to mitigate these risks through rigorous testing and safety protocols.
5. How will China's space launch program impact the global space industry?
China's growing space launch capabilities and ambitious plans for space exploration are expected to have a significant impact on the global space industry. The country's ability to provide cost-effective launch services and develop advanced spacecraft technologies could make it a major player in the international space market.

With World Malaria Day approaching, it is important to understand the severity of this disease and the steps one can take for a speedy recovery. This year's theme, "Malaria Ends With Us: Reinvest, Reimagine, Reignite," aims to re-energize efforts towards eliminating malaria. From getting enough rest to staying hydrated and following proper nutrition, these tips can help in the treatment of malaria. Adhering to prescribed medication and seeking follow-ups with healthcare providers are also crucial for a full recovery.

A diverse group of individuals, including a genius with the world's highest IQ, a psychic with a museum in Tel Aviv, a skeptic Italian physicist, a researcher of the transition between life and death, and a biologist and writer, share their unique perspectives on the enduring mystery of what happens after we die. While some believe in an afterlife and the possibility of reuniting with loved ones in a different dimension, others dismiss such notions as fear-driven or scientifically implausible. Despite the conflicting viewpoints, the curiosity and debate surrounding this timeless topic continue.
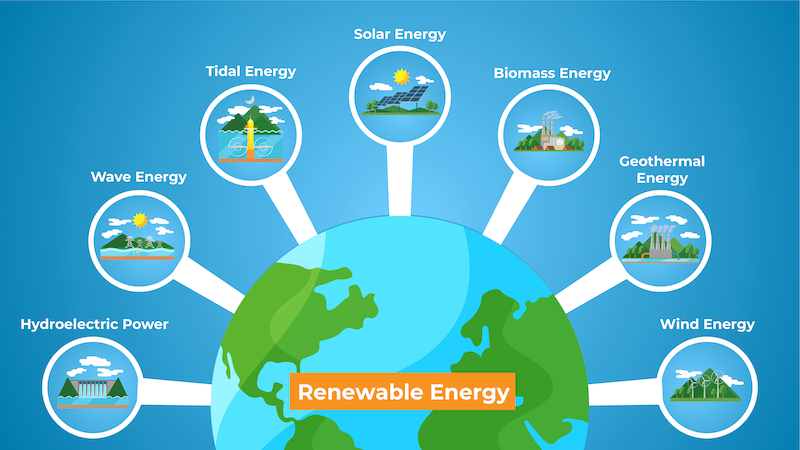
As the world celebrates Earth Day, environmentalists are emphasising the need to shift towards renewable energy, particularly solar energy, to combat the ongoing climate crisis. With the theme 'Our Power, Our Planet', the focus is on raising awareness about the adoption of natural resources. Renewable energy is crucial for safeguarding natural resources and local communities, and experts are calling for the rapid transition to clean, sustainable sources like solar and biomass. The state of Telangana has abundant sunlight making solar energy a viable option, and it is essential for the government to introduce innovative initiatives to promote its adoption across all sectors. By embracing renewable energy, we can contribute to a greener tomorrow for our planet.

Professor Ning Zeng of the University of Maryland came up with the idea of burying dead trees instead of burning them to prevent carbon emissions into the atmosphere. Inspired by the durability of ancient wood found in archaeology, Zeng enlisted the help of a farmer in Maryland to bury 100 tons of unused and damaged trees on his property. However, Zeng faces a roadblock from government permits as burying wood is classified as a landfill and requires time-consuming approvals.

Researchers from the University of Helsinki and the Finnish Geospatial Institute have set up a long-term experiment using laser scanning technology to track the growth and phenology of individual trees. The study, the first of its kind, found that species richness, competitive pressure for light, and water availability all play a role in the timing of spring leaf burst and fall leaf senescence. This experiment provides a better understanding of how local factors impact tree growth and phenology, and the results have been published as open data for further research.

At the Beijing International Youth Innovation and Development Forum, experts emphasized the crucial role of young talent in shaping the future of innovation, particularly in rapidly evolving global scientific frontiers. They stressed on the need to trust, guide, and support young innovators in order to strengthen their skills, with Beijing itself fostering an inclusive talent ecosystem. The importance of cross-disciplinary collaboration in addressing global challenges such as climate change and energy security was also highlighted, with emerging technologies like quantum computing and renewable energy being crucial catalysts for progress in this regard.

World Liver Day, observed on April 19, was established in 2010 to raise global awareness about liver health and diseases. With the liver being the second largest organ and playing a crucial role in various bodily functions, the day brings attention to preventive measures and early screening. Additionally, it advocates for eliminating stigma and improving access to treatment for those affected by liver conditions.

On World Health Day, Dr. Swaramya Chandrasekaran, a gynaecologist at Rela Hospital Chennai, reflects on the progress and challenges in maternal and newborn health in India. She highlights the country's commendable decline in neonatal deaths and the success of flagship schemes such as Janani Suraksha Yojana and Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram. However, she also acknowledges the need for consistent quality of care, especially in rural areas, and calls for strengthening community awareness, upgrading infrastructure, and supporting maternal mental health. The adoption of global frameworks and the commitment to no mother or child being left behind further emphasize India's efforts towards a resilient future.

Recent events have sparked conversations among leading geophysicists about the risk of earthquakes in Vietnam, despite the country not being situated on major tectonic belts. Although the likelihood of catastrophic earthquakes is low, Vietnam still faces the potential for significant seismic activity, particularly in the northwest region. With the presence of multiple geological fault lines, some capable of producing earthquakes with magnitudes up to seven, experts urge for seismic hazard assessments and preparedness measures to mitigate potential damage.

On April 2, the world recognizes World Autism Awareness Day, bringing attention to the challenges faced by individuals with autism. The term "autism" was first introduced in 1911 and has been further defined and understood since then. As a wide range of developmental disorders, each diagnosis is unique, making it important to understand and support those on the spectrum. This day aims to raise awareness and promote understanding and support for individuals and their families.