

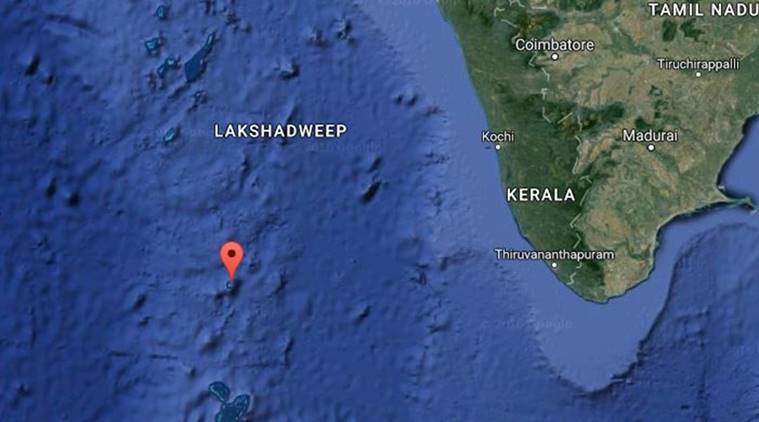
On Monday evening, a 4.5 magnitude earthquake was felt in the Arabian Sea, 270 kilometres from the island of Minicoy in Lakshadweep. The National Center for Seismology reported that the earthquake originated at a depth of 10km at 8.56pm. Luckily, there have been no reports of damages so far. Stay updated with Manorama Online App, the leading Malayalam news source for breaking news on your mobile and tablet.
Earthquake in the Arabian Sea Near Maldives
On Monday evening, an earthquake with a magnitude of 4.5 was felt in the Arabian Sea, 270 kilometers from the island of Minicoy in Lakshadweep. The National Center for Seismology (NCS) reported that the earthquake originated at a depth of 10km at 8.56pm.
Background
The Arabian Sea is a marginal sea of the Indian Ocean, bounded by the Arabian Peninsula and the Indian subcontinent. It is a seismically active region, with several major earthquakes recorded in the past.
In 2011, a magnitude 7.4 earthquake struck off the coast of Pakistan, killing 50 people and injuring over 150. In 2015, a magnitude 6.9 earthquake struck near the island of Mayotte in the Comoros, causing significant damage but no casualties.
Impact of the Earthquake
The NCS reported that there were no immediate reports of damage or injuries as a result of the earthquake. However, residents of Lakshadweep and the Maldives reported feeling the temblor.
Top 5 FAQs and Answers
1. What is the magnitude of the earthquake? A: 4.5
2. Where was the epicenter of the earthquake? A: 270 kilometers from Minicoy in Lakshadweep
3. How deep was the earthquake? A: 10km
4. Did the earthquake cause any damage or injuries? A: No
5. Is there a risk of aftershocks? A: Yes, there is a possibility of aftershocks, but they are likely to be weaker than the main earthquake.

In a recent family vlog, Indian celebrity couple Shoaib Ibrahim and Dipika Kakar shared their "natural" hair care routine for their son, using a homemade mask made with rice flour, flax seeds, and coconut oil. However, experts warn that what works for adults may not be suitable for babies, whose sensitive skin and scalp could react to the ingredients. While the ingredients may improve hair texture, they do not necessarily promote hair growth. Instead, a healthy diet and good scalp care are more important in maintaining healthy hair.

A recent consumer study has found multiple brands of soft contact lenses in the U.S. to contain "forever chemicals" that can be harmful to both the body and the environment. The study, conducted by the nonprofit organization Environmental Health Sciences, tested 18 varieties of popular contact lenses and found all of them to contain markers for PFAS. Brands such as Acuvue, Alcon, and CooperVision were among the list of affected products. This news serves as a cautionary lesson on the potential risks of overusing contact lenses.

On the birth anniversary of Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam, the ‘Missile Man’ of India, tributes pour in on social media celebrating his life, vision and impact. A visionary scientist, inspiring leader and true patriot, Dr. Kalam's humility, compassion and constant interaction with students continue to inspire generations. His tireless efforts in defense, science and youth empowerment have strengthened India's path towards self-reliance and his legacy continues to motivate young minds to dream big and work hard for the nation.

Recent studies have found that extreme heat, particularly when combined with high humidity, can have a significant impact on mental health. A study in India showed that when wet bulb temperature exceeded 27°C, the probability of reporting severe depression increased by 0.5%, even when the temperature was slightly lower. This finding is consistent with global reviews that have linked high temperatures to mood disorders, increased hospital admissions for psychiatric conditions, and even elevated suicide risk. The Lancet has also published evidence that rising temperatures worldwide are a growing threat to emotional and cognitive health.

In a meeting with university officials in Udaipur, Rajasthan Governor Hari Bhau Bagde stressed the importance of incorporating India's ancient knowledge traditions into academic research. He highlighted the deep repository of knowledge in India since ancient times and urged scholars and scientists to draw upon this tradition in their work. Bagde also suggested making ancient texts available in university libraries for study and research purposes, in order to shape the intellectual abilities and love for the nation among the younger generation.

John Clarke, Michel H. Devoret, and John M. Martinis have been awarded the 2025 Nobel Prize in Physics for their pioneering research into quantum mechanical tunnelling. Their discovery has opened new possibilities for quantum technologies, and will be formally presented on December 10, the anniversary of Alfred Nobel's death. This announcement follows the tradition of recognizing transformative contributions to science, and the award carries a prestigious prize of 11 million Swedish kronor.

The US-Japanese trio of Mary E Brunkow, Fred Ramsdell, and Shimon Sakaguchi have won the 2025 Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine “for their discoveries concerning peripheral immune tolerance". Through their research, they have shown how the immune system is kept in check and why serious autoimmune diseases do not affect everyone. Sakaguchi found a new class of T cells, while Brunkow and Ramsdell discovered the explanation behind a specific mouse strain's vulnerability to autoimmune diseases. Together, they have significantly advanced our understanding of immunology and autoimmune diseases.

Indian astronaut Shubhanshu Shukla, who recently completed a 20-day space mission, shared his insights and experiences at the convocation ceremony of Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam Technical University. He highlighted the importance of patience, focus, and the inevitability of change in achieving success, and urged the graduating class to actively contribute to shaping a fearless and ambitious India.

The Regional Meteorological Centre (RMC) in Chennai has issued a weather alert for parts of Tamil Nadu, with thunderstorms and light to moderate rainfall expected on Saturday. The alert was issued due to the strengthening of a cyclonic circulation in the Bay of Bengal, which is likely to intensify and form a low-pressure area. The system is expected to affect Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, and Karaikal, with some areas experiencing heavy rainfall and gusty winds. The public is advised to stay updated and take precautions, especially in hilly and western districts.

As a step towards advancing India's deep-sea research capabilities, the Union Science Minister announced a landmark contract with the International Seabed Authority to conduct mineral exploration in the Indian Ocean for the next 15 years. This move will not only help India in expanding its scientific knowledge about the deep sea but also has the potential to strengthen its position as a leading player in the international seabed mining industry.